
Startup Jedi
We talk to startups and investors, you get the value.
Peer Review is a method of mutual evaluation in which professionals from the same field can evaluate each other’s work.

Startup Jedi
We talk to startups and investors, you get the value.
Peer Review method is popular in various spheres of life. In science it is known as peer review — the study and evaluation of scientific works by specialists working in the same field with the author. In medicine, doctors can assemble a consilium to evaluate the quality of treatment, make “work on errors” or learn new methods for themselves. In the technical field, engineers conduct an expert technical assessment, a form of engineering expertise for which specialists from the same fields are invited to identify defects and propose solutions.
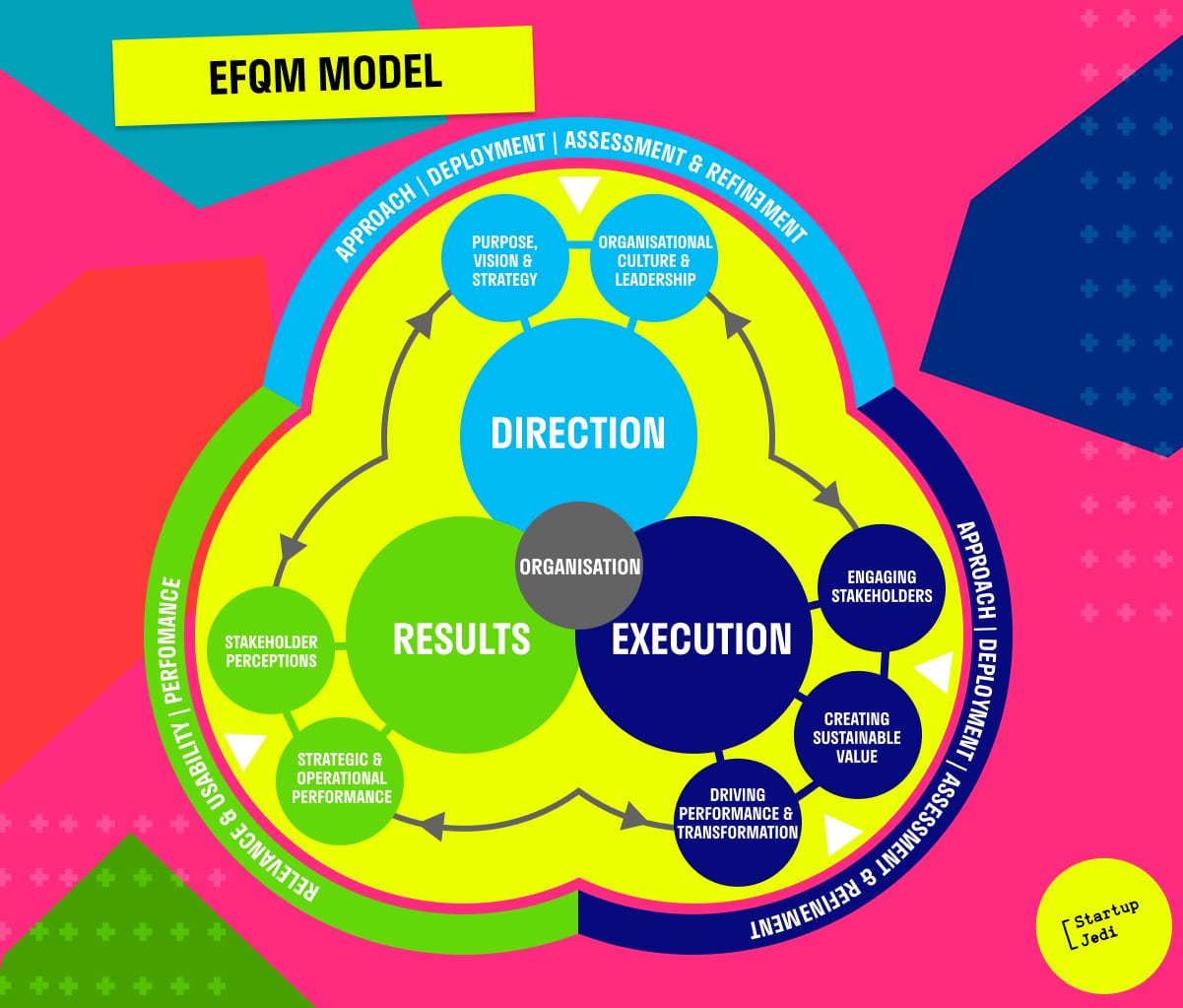
The model developed by the European Foundation for Quality Management (EFQM), which helps companies to identify their weaknesses and strengths, can be used to apply Peer Review to the performance assessment of organizations.
The model includes three main blocks:
direction (goal setting);
actions (execution);
results.
The main task of the model is to help the company realize and answer three main questions that are important for sustainable and effective development:
Why? Why does the company exist? What is she doing? What is its purpose, strategy, mission? (Direction).
How? Why does the company do this? What means and opportunities does it use to achieve its goals and create sustainable corporate values? (Actions).
What? How effective are the actions taken? Are the needs of all stakeholders met? (Results).

Depending on the direction of the company, the research organizers prepare a questionnaire covering all blocks of the model. There is a field in the questionnaire where the research company can add its questions to the experts invited by the organizers to study the received answers. During the questionnaire the company analyzes its activities, identifying its advantages and disadvantages. The completed document is sent to the experts for evaluation.
For ease of reference, the organizers will set up a cloud-based repository to house all documents that will be available to each participant in the study.
So the Peer Review algorithm looks the following way:
The organizers prepare a document-questionnaire with questions for the evaluated company — “the owner” and send it to the “owner”.
The “owner” fills out the questionnaire in writing. He can attract employees from different departments to explain all the subtleties of the organization of processes in the most understandable way.
Then the “owner” sends the completed questionnaire to its future “guests” — companies-experts a few weeks before their arrival.
“Guests” thoroughly study the document to prepare for the visit and work out all potential recommendations or questions for the “owner”.
During the visit of “guests” the host is given time for a live presentation. You can take a tour, invite other people interested in the process, like stakeholders or customers.
After the presentation “guests” are removed to a separate audience for discussion and rendering a “verdict”.
Then “guests” and “hosts” meet to “guests” share their observations and give their recommendations.
After a while, the organisers request a report to assess whether the experts' recommendations were useful, what changes the company has made and whether this peer review method is useful for improving the performance of the host company.
During the evaluation, the economic, political and social conditions of the system in which the company operates should be taken into account in order to obtain the most effective results.

Here is an example of some questions from a questionnaire developed by Swedish Incubators & Science Parks (SISP) in 2016-2017, which adapted the EFQM model for expert evaluation of business incubators and conducted its research.
Guide
What are the actions of management to define clear goals and plans for the development of the company?
How are key performance indicators and goal fulfillment tracked?
Team
Is there communication between management and the team?
Is there room for individual development of each employee? How do you evaluate each employee’s KPI?
How are new, highly qualified personnel attracted?
Financing
How is the financing system organized, what sources of income are used? Are there any connections with the networks of "business angels"?
Plans and strategies
Is there a process of discussing development plans between management and investors?
How does the decision-making process work in the company?
How clearly is the organization's mission outlined? Are employees aware of the goals and objectives of the organization?
Partners and resources
How is the incubator integrated into the regional business community? Are different projects being implemented locally, nationally or internationally?
How easy is it for a startup to get access to the necessary infrastructure: office space, services?
Business development and client engagement
How are new ideas attracted?
What are the requirements for entry into a business incubator?
How is the progress of each startup monitored?
What is the procedure for exiting a business incubator?
Results
Are activities carried out with startups coming out of the incubator, and are contacts maintained?

One example of the use of the Peer Review method among business incubators was the IRIS project, created by a team from the Dalarna Science Park in Sweden with the support of the Swedish Institute under the Interreg Baltic Sea Region programme. The organizers assembled a team of 14 business incubators from Sweden, Latvia, Lithuania, Russia, Germany, Poland, Estonia, Finland, Denmark. In addition to the main goal of sharing experience between business incubators, the organizers for the first time applied Peer Review at the international level.
After the end of the project, the participants noted that the main advantage of Peer Review was the opportunity to look at themselves "from the outside", to see their work processes from an international perspective.
In preparation for the visit of the experts, each of the participating hosts was able to discuss all the relevant problems with colleagues and learn something new for themselves. The exchange of experience and new acquaintances have led to the creation of new projects.
To get acquainted with the results of the study, as well as to download a sample document with questions that was created by the organizers for the participants of the project, please click here.

During the preparation of the answers to the questions you can find something new about your company, both positive and negative.
Sharing experiences between similar organizations can help solve the problem (try asking a colleague, perhaps someone has already faced the problem).
Visiting new companies helps create new ideas.
The whole process takes place in a comfortable and friendly atmosphere, as the experts come not to harass or frighten you, but to help and inspire.
The focus of the experts is precisely on the strengths of the company, they will tell in which direction to move forward.
New acquaintances = new opportunities for joint cooperation.
Facebook: facebook.com/StartupJedi/
Telegram: t.me/Startup_Jedi
Twitter: twitter.com/startup_jedi
Comments